What is Website Structure?
Website Structure is what a website looks like. One of the most important aspects of a website structure is its navigation. Also commonly referred to as sitemap, Navigational elements are those items that let users jump around to different pages on the site.
Website structure is the way that a website is divided up into pages. Structuring a website logically will make it possible for people to find and visit the pages that are most important to them. It consists of how content is arranged about each other and how it impacts the users’ experience when interacting with the page or site.
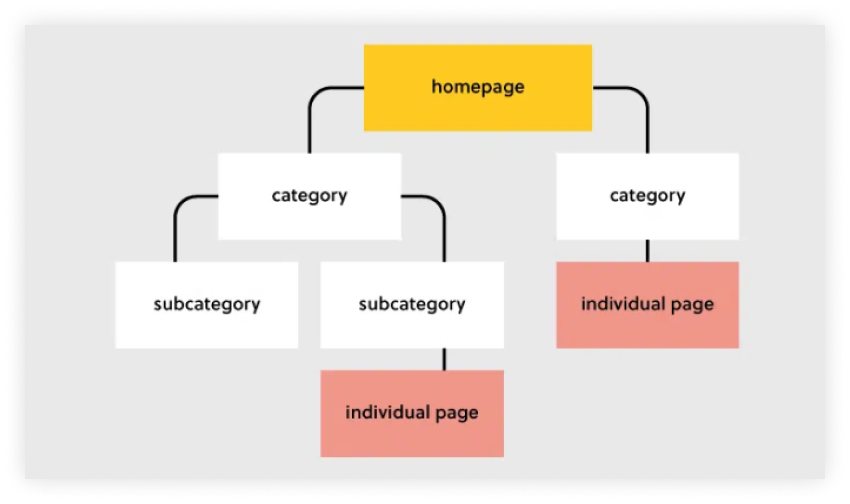
(source: UXpin )
What is the Importance of Website structure?
We all know the importance of a website for a business. The importance of website structure cannot be overstated, as it plays a crucial role in determining the user experience, SEO performance, and overall success of your website. Here are some key reasons why paying attention to your website structure is essential:
- Smooth User Experience: A well-structured website is easier for visitors to navigate. When users can quickly find the information they’re looking for, it leads to a positive user experience. This, in turn, encourages them to stay longer and explore more of your website.
- Sitelinks: Sitelinks are the additional links displayed beneath your website’s main search result in Google. Sitelinks show your domain and several internal URLs arranged below when they are featured in the SERP. Google is more likely to generate sitelinks for your website if it has a well-organised structure. They distinguish your website in search engine results and can raise CTR.
- Improve Crawling: Search engine crawlers, like Googlebot, visit websites to index their content. An organised website structure makes it easier for these crawlers to understand the hierarchy and relationships between pages. When your site is easy to crawl, search engines can index your pages more efficiently. This, in turn, increases the chances of your content ranking well in search results.
- Conversion Rate Optimization: A well-structured website can influence the decision-making process of visitors. Call-to-action buttons, forms, and other elements are strategically placed to guide users towards desired actions, such as purchasing or signing up for a newsletter.
- Prevents Competition Within Your Website: A clear website structure helps prevent competition between your pages for search engine rankings. When your pages are organised logically, they’re less likely to compete with each other for the same keywords. This avoids confusion in search engines and ensures each page can rank for its intended keywords, attracting the right audience to the right content.
Types of Web Structures
There are many different types of web structures that you should be familiar with. Web structures come in many different shapes and sizes. They aim to hold a website together, make it easy for visitors to navigate, and help search engines rank your website.
Web structures are classified in two ways: static and dynamic. A static web structure is unchanging, while a dynamic web structure can adapt by adding or removing content throughout the day.
The web has developed from a single-page website to a full-fledged content management system. There are many types of web structures that you can use for your purposes.
1. Hierarchical structure
- A hierarchical structure is a structure that has a clear hierarchy or order starting at the home page and moving down pages in order until you reach the bottom.
- This type of structure is sometimes referred to as “tree-structured” because it resembles a tree that grows from the ground upwards with branching levels.
- The main advantage of this type of Web structure is that it’s easier to find specific topics.
- It is the most common type of Web structure. It breaks out information into categories like subfolders in a computer file system. For example, our website RankHawn.

2. Sequential Structure
- In a Sequential web structure, users navigate through the website in a predefined order, typically starting from the first page and progressing sequentially to subsequent pages.
- The flat organisation, also known as linear structuring or sequential model, is on one level with no sublevels or branching levels. There is usually only one way to move from one page to another.
- The sequential model guides users through a step-by-step process. It’s particularly useful for instructional websites, online forms, tutorials, and e-learning platforms. For example, Coursera
3. Database website structure
- A database website structure, also known as a dynamic web structure, is a type of website architecture that relies heavily on a database to store, retrieve, and present content to users.
- This structure is commonly used for websites that involve large volumes of data, user-generated content, and frequently updated information. For example, Pinterest
4. Matrix website structure
- The matrix website structure is characterised by a network of interconnected web pages, allowing users to navigate between related content easily. This website structure is also known as the webbed model.
- The matrix model arranges content in a grid or table, allowing users to explore multiple options simultaneously. For example, BBC.
How to Choose the Best Structure For Your Website?
Choosing the best structure for your website can be a difficult process. It’s important to recognise that there is no “right” answer, as all structures have strengths and weaknesses. The way you structure your website will likely depend on several factors; here are the key factors that might help you choose the best structure for your website:
- Define Your Goals: Decide on the main goal you want visitors to accomplish when they come to your site, for example buying something or seeking more information about your product or service. Once you know what you want it to do, it becomes easier to adjust or adapt the design to match this purpose.
- User Journey Mapping: Once you know what your visitor’s objective is, start listing all the steps they will take from entering your site until they leave with whatever it is they came for. A good way to do this is by using a navigation map, which lets you create individual pages and link them together with arrows showing where people can go next, for example, page 1 > page 2 > page 3 > page 4 > page 5.
- Content Hierarchy: You must plan out how you will organise the content that you want to post on your website Use clear categories, subcategories, and tags to help users easily find relevant information.
How to Have a Good Website Structure?
A well-structured website is crucial for providing a positive user experience, improving SEO, and ensuring that visitors can easily find the information they’re looking for. Here are the essential elements of website structure to create a good website structure:
Layout and Structure: The first thing to consider is how the layout of your website is going to work. In this case, you will need to think about the best way your site will be structured. There are many ways in which a website can be designed and laid out, but you must use the one that suits your business needs.
Content: If there are any articles or blog posts that need writing for your website, this should be taken into consideration before anything else. Without the necessary content for your site, there is not much point in setting up a layout or structure.
Navigation: Have a clear and user-friendly navigation menu, typically located at the top or side of your website. Use intuitive labels for menu items, and limit the number of items to avoid overwhelming visitors. Consider using drop-down menus for subcategories or related content. Check out an example of an e-commerce website, AJIO.
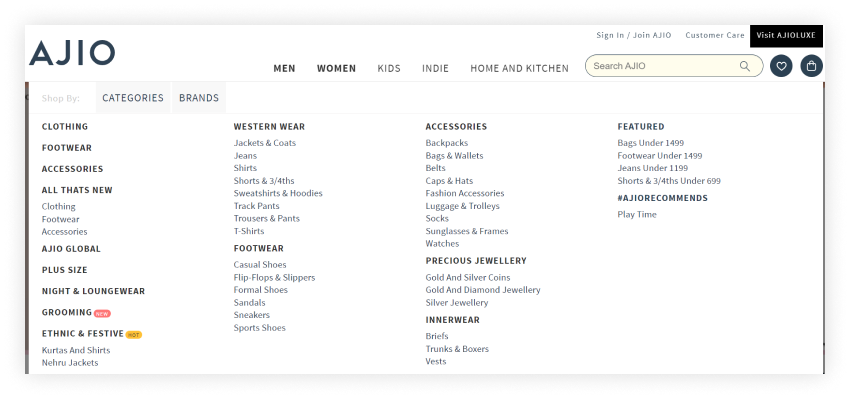
Categories and Subcategories: Organise your content into logical categories and subcategories. Ensure that categories are easy to understand and reflect the main topics of your website. Use clear and concise category names to make navigation straightforward.
URL Structure: In addition to having effects on SEO, URL structure has a big impact on how a website is organised overall.
- Keep URLs descriptive, short, and user-friendly.
- Use hyphens to separate words (e.g., “example.com/about-us” instead of “example.com/aboutus”).
- Avoid using special characters, symbols, or excessive parameters in URLs.
- Use a consistent and logical hierarchy for pages within your website.
- Example: Instead of “website.com/page123,” use “website.com/men/shirts/casual-shirts.
Internal Links: Include internal links within your content to connect related pages and improve user navigation. Use descriptive anchor text to let users know what to expect when they click the link. Avoid excessive linking, as it can be distracting or seem spammy. Internal links join the website’s many pages, creating linkages between them and enhancing navigation.
Breadcrumbs: Breadcrumbs are a link trail showing users their current location on your website. They make it easier for users to navigate to higher-level pages or categories. Breadcrumbs also help search engines understand your site structure.
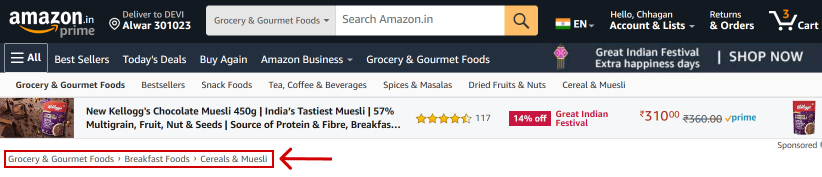
Sitemap: Create an XML sitemap for search engines to help them index your website efficiently. An HTML sitemap, usually linked from your homepage, aids user navigation by providing an overview of your site’s structure.
Tags: Use meta tags, such as title tags and meta descriptions, to provide concise and informative summaries for each page. Ensure your tags are unique and accurately represent the content on each page. Optimise meta tags for search engines and users. Tags are a helpful tool for organising comparable content on a page.
Homepage: Your homepage is the main entry point for most visitors. Keep it clean and user-friendly. Include a clear and concise introduction to your site’s purpose and content. Highlight important content and provide easy access to key sections.
Individual Page: Each page should focus on a specific topic or idea. Use headings, subheadings, and bullet points to break up content and make it easier to scan. Include relevant images, videos, or other media where appropriate.
Conclusion
Optimising your website structure is a critical step in achieving SEO excellence. It’s worth noting that you have two options for improving your website structure: you can either handle it in-house or outsource it to experts in the field.
Remember that site structure is an ongoing process. Regularly review and update it as your content grows and user needs evolve. Additionally, stay informed about changes in SEO best practices and user expectations to keep your site structure optimised for both search engines and visitors.



Leave A Comment